Ripple Filter
One of the main goals of protons or carbon ions beam therapy is delivering a uniform dose to the target, minimizing the number of required energy steps.
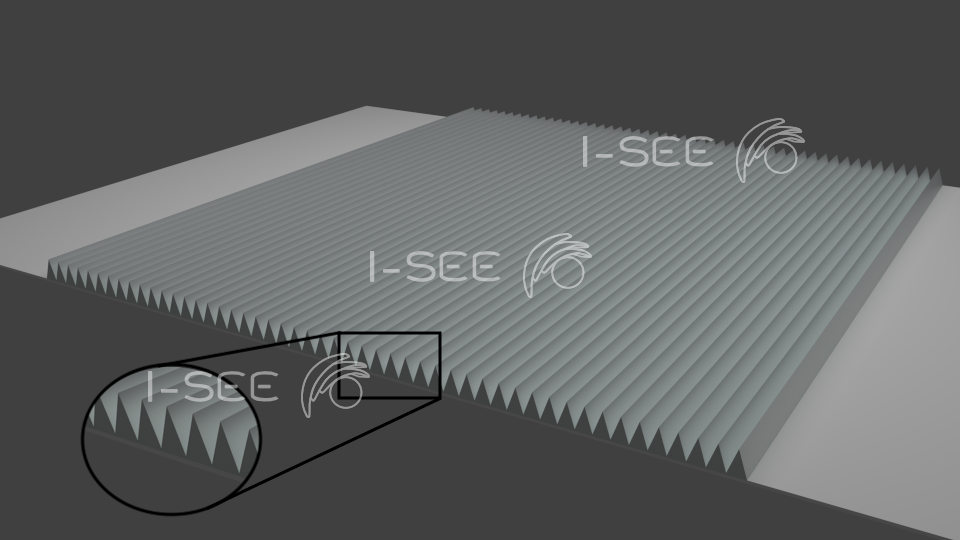
i-See designed specific components, called Ripple Filters, able to spread around the Bragg peak preserving its gaussian shape. This device is located into the nozzle of the beam delivey line at a given distance to the target isocenter.
We studied the impact of the design of the ripple filter by means of Monte Carlo simulations, implemented using the package Geant4, subsequently validated at CATANA and CNAO centers.
RiFi for particle therapy
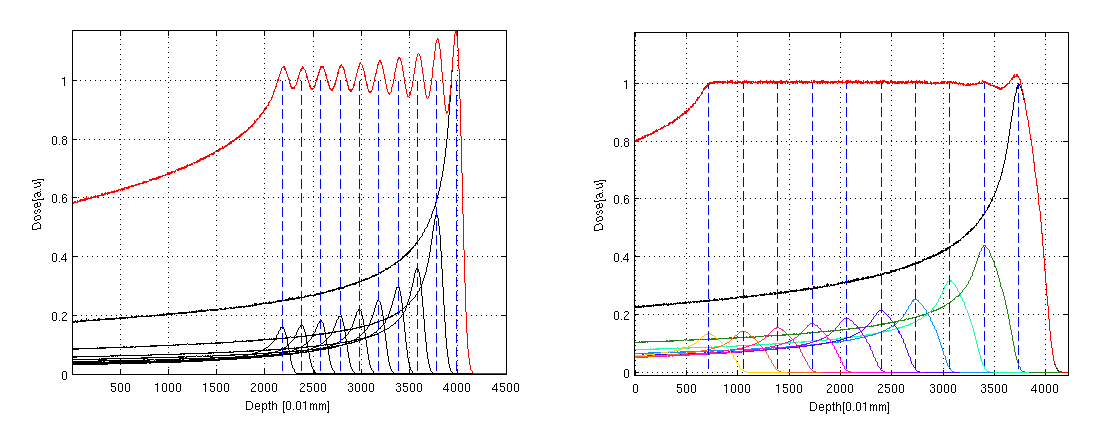
In particle therapy, in order to achieve an acceptable homogeneity of the Spred Out Bragg Peak (SOBP), the pristine peaks need to be broaden at least few millimeters. The use of a properly designed ripple filter, in particular in conjunction with active scanning techniques for dose delivery, helps to reduce the numbers of energy switches necessary to obtain a smooth SOBP, leading also to shorter overall irradiation times.
RiFi for radiobiology
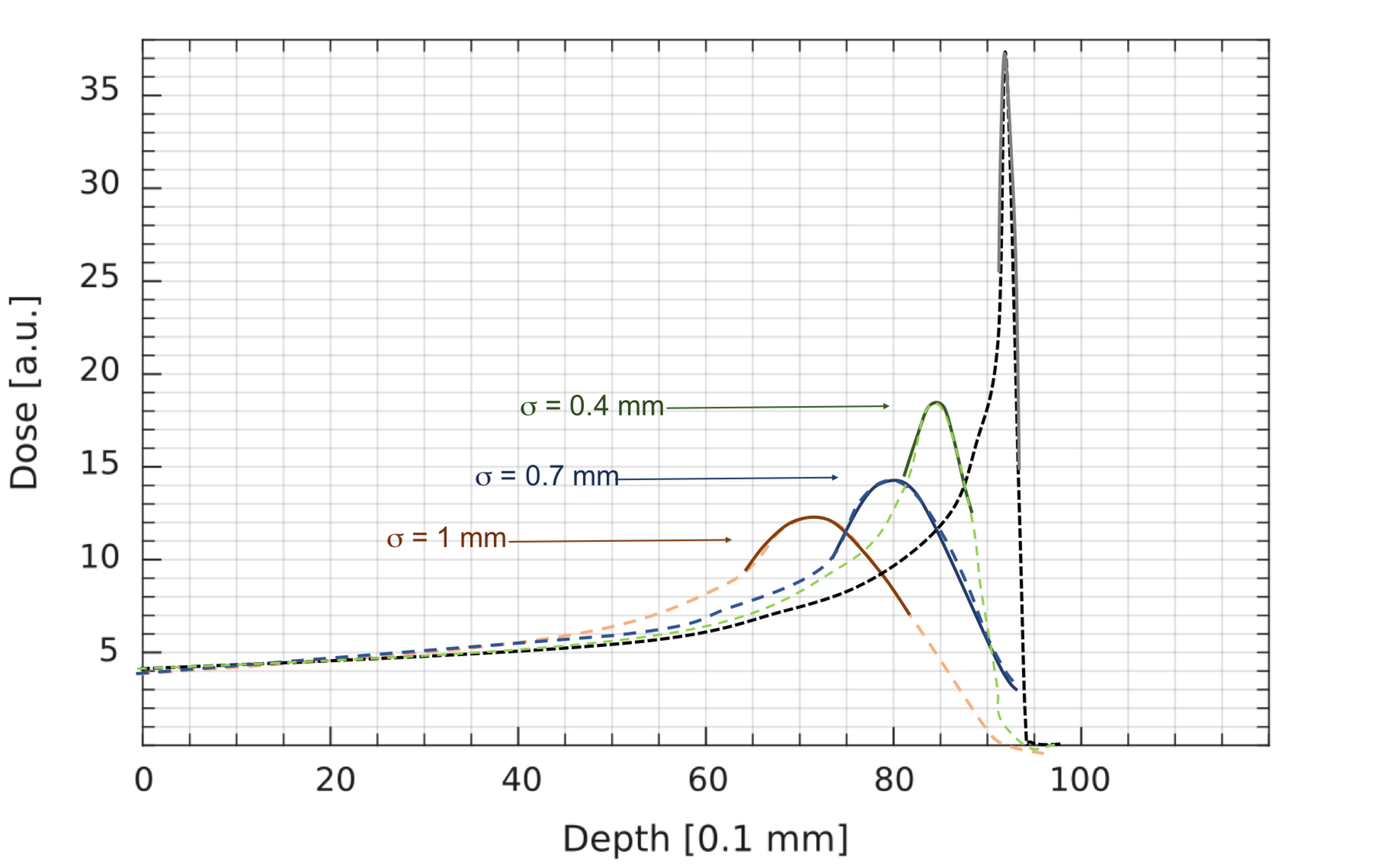
The radiobiological cell survival measurements at the Bragg peak have the problem of uncertainties in the positioning of cell samples in the peak region. This is due to the very sharp shape of the maximum of energy deposition for carbon ion beams and also proton beams at low energies.
We designed for this specific purpose a special ripple filter in order to produce a small broadening of the peak region to allow a more reliable positioning of cells samples.
RiFi WebApp
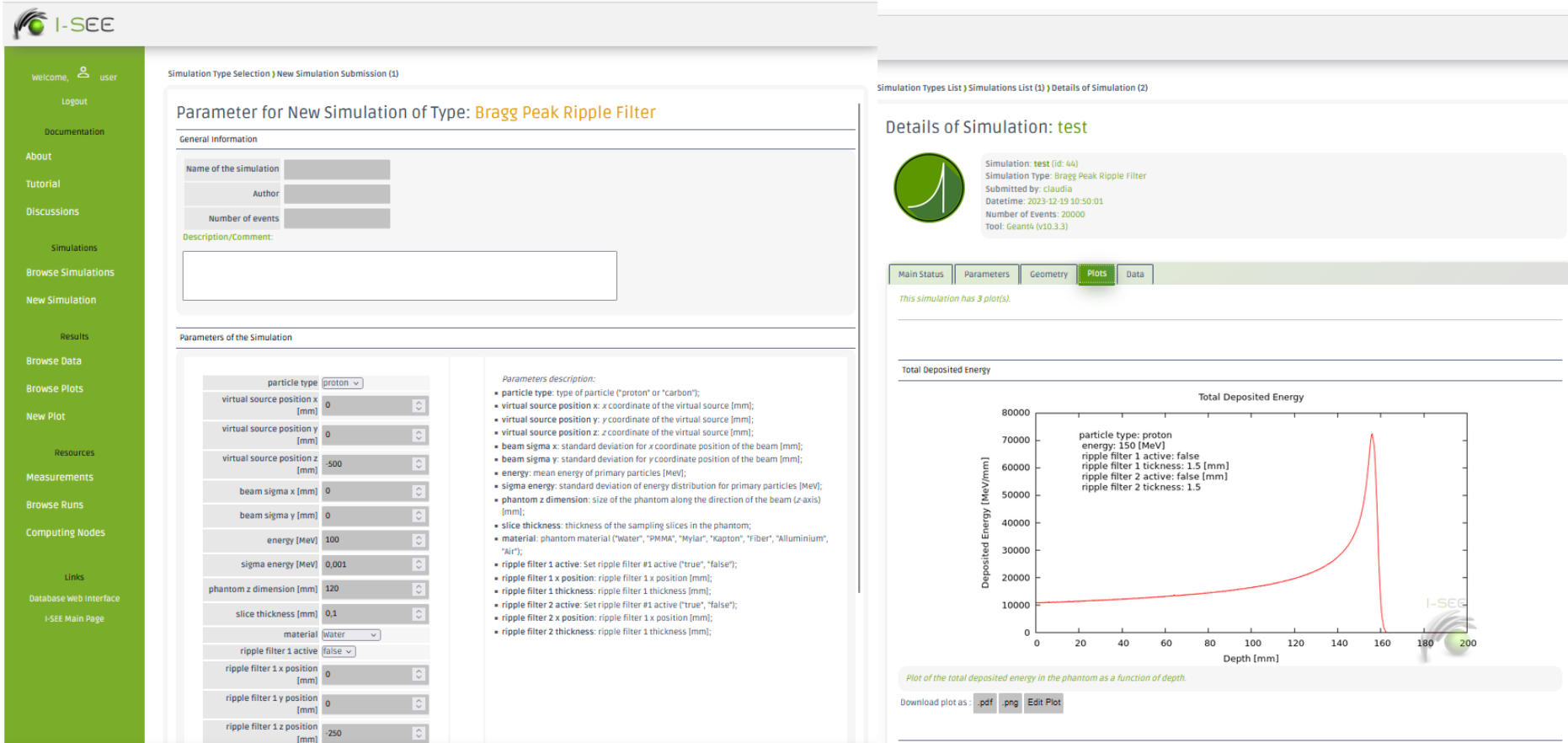
RiFi web app is a Monte Carlo online tool that we developed to simulate monoenergetic ion beams through one or two ripple filters. The application can be accessed completely remotely on browsers, via a simple link. User can submit and browse its own simulations and then collect, share and analyze data.
RiFi WebApp key features:
- Change simulation input parameters (source, nozzle configuration, phantom properties, number of histories)
- Submit simulation
- Collect and analyse resulting Bragg peak in terms of range, FWHM, distal falloff, peak-to-plateau ration, build-up region, lateral penumbra, fragment distribution and other characterizing parameters.